New Breakthroughs in the Fight Against Cancer
Cancer research has made huge progress in recent years, bringing hope for better treatments and possibly even a cure. Breakthroughs in areas like immunotherapy, early detection, and targeted therapies are changing how we approach cancer care. These advances are opening new doors for more personalized and effective treatments. Immunotherapy, for example, helps the body’s immune system fight cancer more effectively. Early detection methods are making it easier to catch cancer in its earliest stages, improving survival rates. Targeted therapies are also allowing doctors to zero in on cancer cells without harming healthy tissue. These key developments are making a big difference in cancer treatment, giving patients and doctors new options and hope for the future.
1. Immunotherapy Advancements
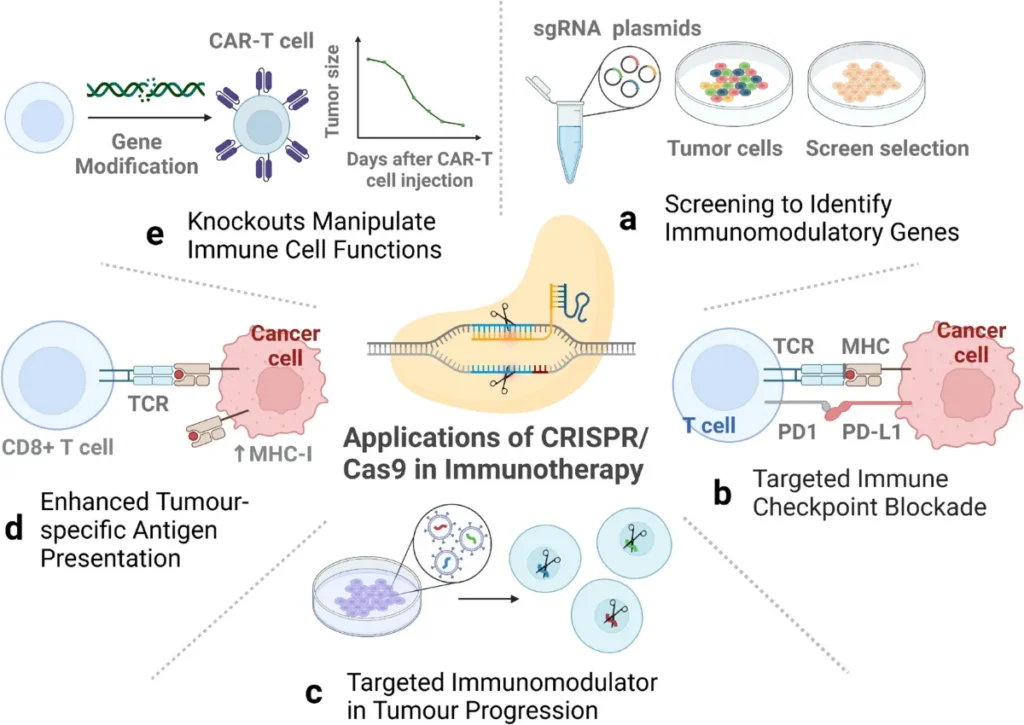
Immunotherapy is a cancer treatment that strengthens the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Recent breakthroughs have focused on making these treatments more effective, especially by personalizing them for each patient. One of the main advancements is checkpoint inhibitors, which help “release the brakes” on the immune system, allowing it to better target and destroy cancer cells. New types of checkpoint inhibitors, like T-cell engagers, are showing promise in treating cancers that were previously difficult to treat, such as triple-negative breast cancer. Another exciting approach is CAR-T cell therapy, where doctors reprogram a patient’s T cells to attack cancer cells. Recent improvements in CAR-T therapy are making it more successful, particularly for blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. Bispecific antibodies are also being developed to bind to two different antigens at once, helping the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. These antibodies are being tested in clinical trials and are showing potential for treating both blood cancers and solid tumors. Together, these innovations in immunotherapy are making cancer treatments more precise, personalized, and powerful than ever before.
2. Targeted Therapies
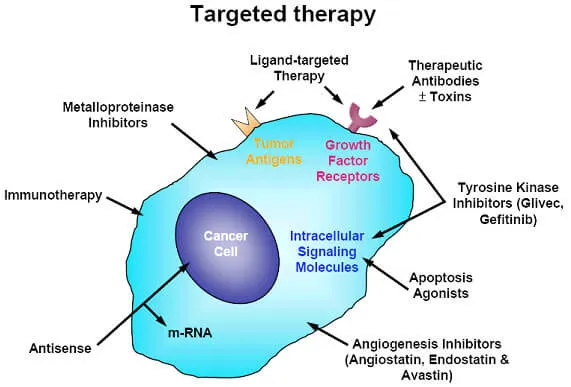
Targeted therapies focus on specific genes or proteins that help cancer cells grow and survive. Recent breakthroughs have led to more precise drugs that can attack cancer cells with fewer side effects. One important advancement is the development of targeted drugs for genetic mutations. By using gene sequencing, researchers can identify mutations driving cancers and create drugs to target them. For example, drugs targeting BRAF mutations in melanoma and EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer are showing promise. Another breakthrough is next-generation targeted therapies, which focus on cancer-specific pathways and molecules. Drugs like PARP inhibitors are opening up more treatment options, especially for cancers like ovarian and breast cancer. These advances are helping to create more personalized treatments, making cancer care more effective and less harmful to healthy cells.
3. Early Detection and Liquid Biopsies
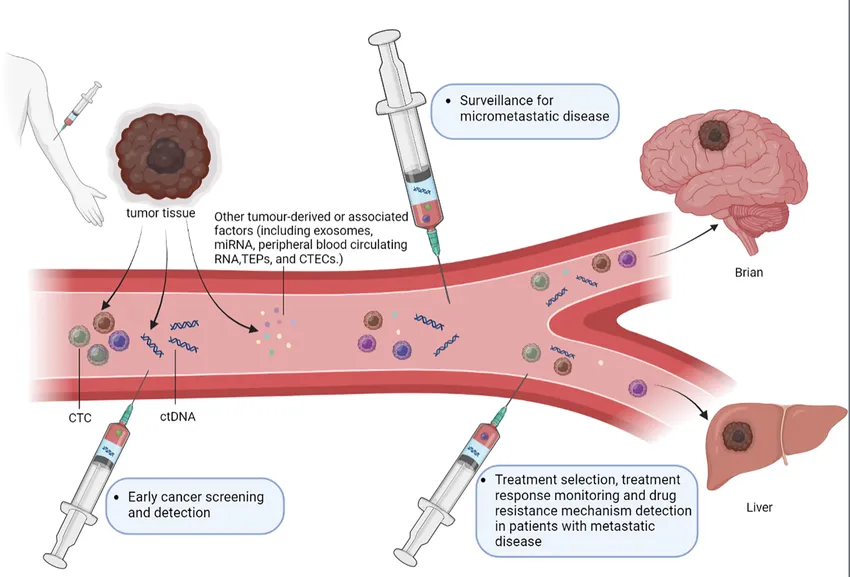
Early detection plays a crucial role in improving cancer survival rates, as catching cancer early increases the chances of successful treatment. Liquid biopsies have emerged as a game-changer in this area. These non-invasive tests detect cancer-related genetic material found in blood samples, providing a way to identify cancer before it becomes symptomatic. Advances in liquid biopsy technology have made it possible to detect multiple types of cancers at earlier stages, even before symptoms appear. This breakthrough could significantly improve outcomes by allowing doctors to catch cancers when they are most treatable. In addition to early detection, liquid biopsies are also enhancing precision diagnostics. By identifying cancer-related mutations, doctors can tailor treatment plans to each individual patient, improving the effectiveness of therapies. This means that treatments can be more personalized, targeting the specific characteristics of the cancer, which helps minimize side effects and improve patient outcomes. Liquid biopsies are quickly becoming a vital tool in the fight against cancer, offering hope for earlier and more targeted treatments.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cancer Research
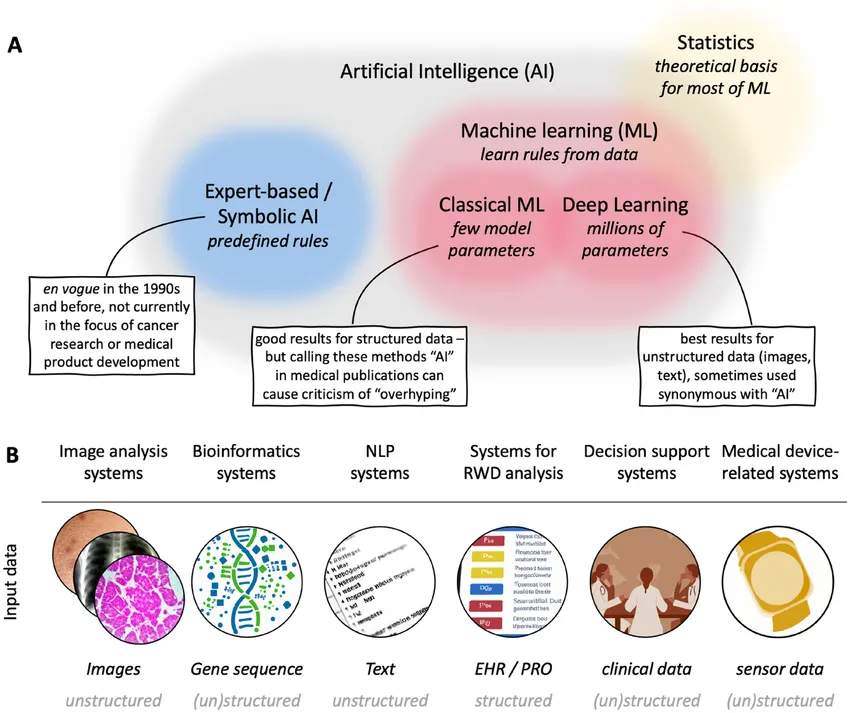
AI and machine learning are transforming cancer research by improving diagnostic accuracy, drug discovery, and treatment planning. In medical imaging, AI helps analyze CT scans and MRIs faster and more accurately than human doctors can. This enhances early tumor detection and improves precision in determining cancer stages. AI is also making a big impact in drug discovery. It can quickly screen vast databases of molecules, helping researchers find new cancer drugs more efficiently. This speeds up the process of moving new treatments from the lab to clinical trials, potentially shortening the time it takes to bring new therapies to patients. AI’s ability to process and analyze large amounts of data is revolutionizing how cancer is diagnosed and treated, offering more hope for faster and more effective treatments.
5. Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines are designed to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. While vaccines like the HPV vaccine for cervical cancer have already been successful, new vaccines are being developed for other types of cancer. Therapeutic cancer vaccines aim to treat cancer by training the immune system to target specific cancer cells. Though still in the experimental stage, these vaccines have shown promise in treating cancers like melanoma and lung cancer. Researchers are also working on personalized cancer vaccines, which are tailored to a person’s unique cancer mutations. This approach could boost the immune system’s ability to target cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue, offering a more precise and effective treatment option.
6. Advances in Radiation Therapy
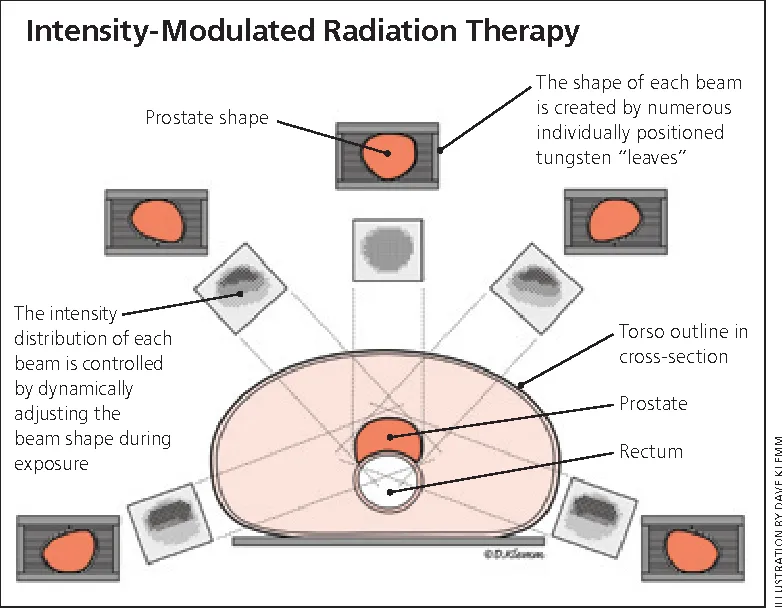
Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells, is continually improving with new techniques that make it more precise and effective. One such advancement is proton therapy, which uses charged particles instead of traditional X-ray radiation. This allows doctors to target cancer cells with much greater precision, reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Proton therapy is especially helpful for treating cancers in sensitive areas, like the brain and spine, where preserving healthy tissue is crucial. Another innovation is Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT), which delivers high doses of radiation to tumors with extreme precision. SBRT can treat tumors in just a few sessions, minimizing side effects and reducing treatment time. These advancements in radiation therapy are making it possible to provide more targeted and effective treatments, improving outcomes for patients with various types of cancer.
7. Gene Editing and CRISPR
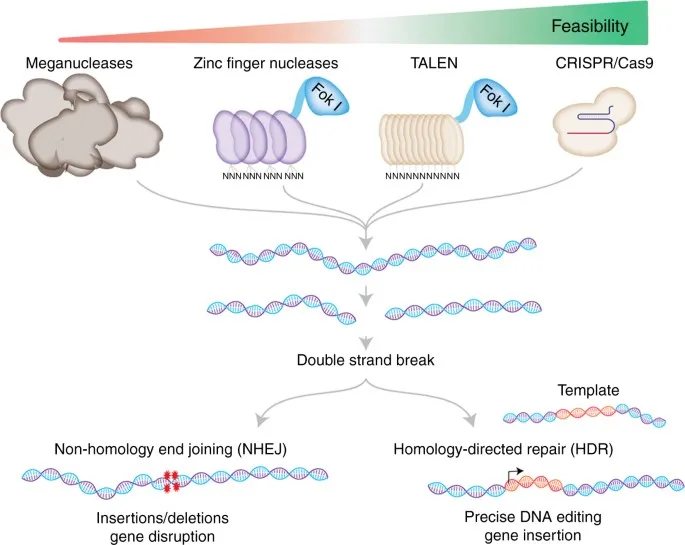
Gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 are transforming cancer research by enabling scientists to directly modify the DNA of cancer cells. This breakthrough allows for the potential to stop tumors from growing by altering the genes inside cancer cells. Early trials of gene therapy have shown promise, and researchers are now focusing on using gene-editing technologies to repair damaged genes in healthy cells, potentially preventing cancer before it starts. CRISPR is also being used in immunotherapy to enhance immune cells, such as T cells, so they can better recognize and destroy cancer cells. This approach could make immunotherapies more effective and targeted, improving outcomes for various cancers. With these advancements, gene editing holds great potential for revolutionizing how we treat and even prevent cancer, offering hope for more precise and personalized treatments in the future.
8. Microbiome and Cancer Treatment
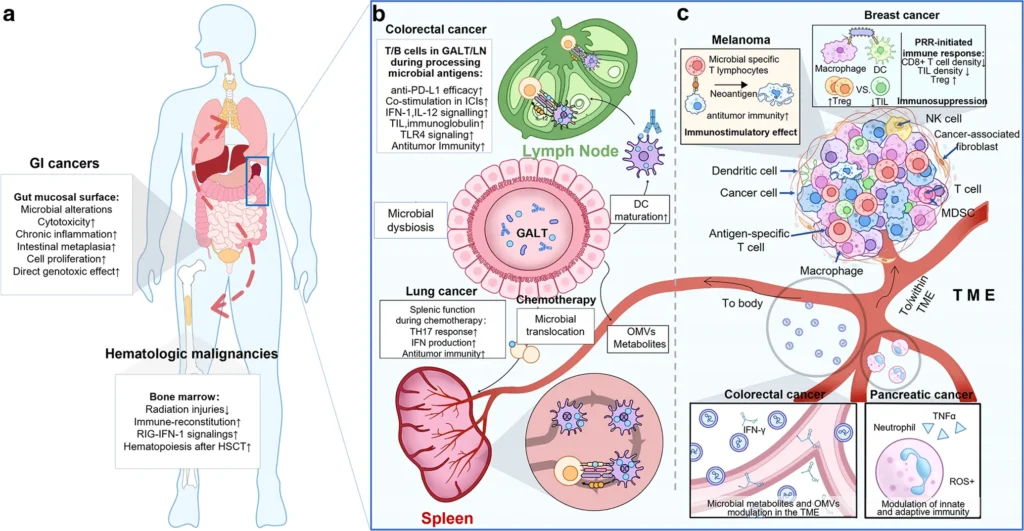
Recent research has revealed that the gut microbiome—the collection of microorganisms in our digestive system—can impact how cancer treatments work. Studies suggest that a healthy gut microbiome may enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapies, like checkpoint inhibitors. Researchers are exploring ways to manipulate the microbiome to improve cancer treatment outcomes. Additionally, microbiome-based therapies, such as using probiotics and prebiotics to balance the microbiome, are gaining attention as potential treatments in cancer care. This new area of research could lead to innovative ways to improve cancer therapy by targeting the microbiome and its role in treatment response.
9. Cancer Drugs Derived from Natural Sources
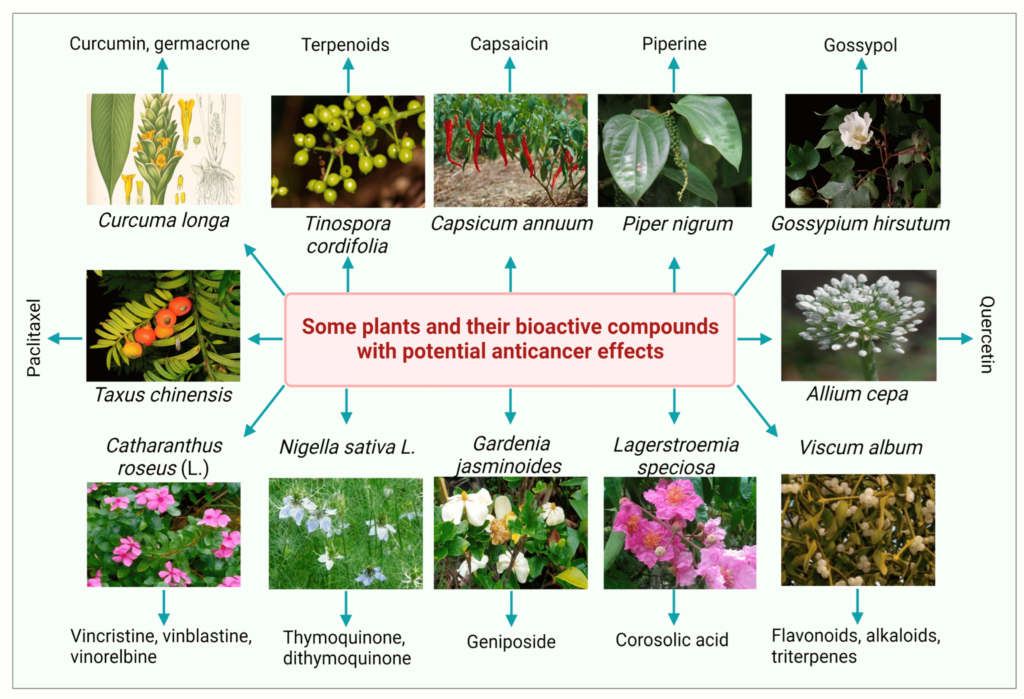
Nature is continuing to offer promising possibilities for cancer treatments. Researchers are looking into new drugs derived from plants, marine life, and other natural sources. Marine organisms like sponges, sharks, and deep-sea microbes have already provided compounds with potential to fight cancer. These natural products are being studied for their ability to stop cancer cells from growing and spreading. Plants, such as the taxus tree, which provides the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel, are still a key source of cancer-fighting compounds. Scientists are now focused on synthesizing these compounds more efficiently and discovering new ones that could offer even better treatment options.
10. Immuno-Oncology Combination Therapies
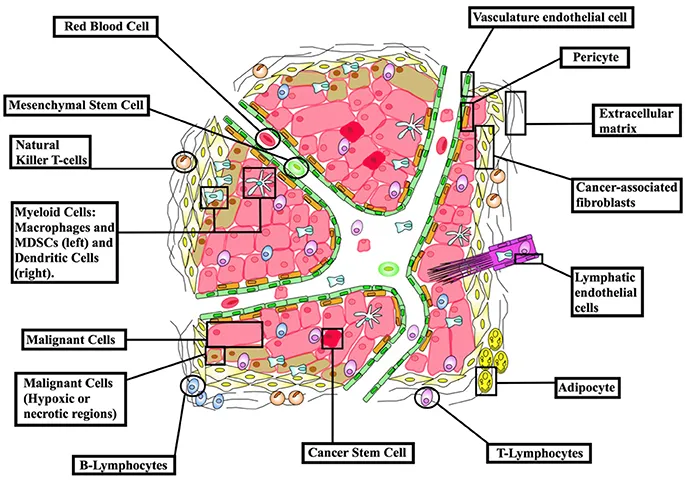
Combining different types of cancer treatments is becoming a key area of research, as doctors look for ways to improve effectiveness. By pairing immunotherapies with chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies, the goal is to enhance how well these treatments work together. For example, combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy has shown better results in some cancers, like lung cancer. This combination allows the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively after chemotherapy weakens them. Similarly, studies suggest that radiation therapy, which damages cancer cells, can work in synergy with immunotherapy to boost the immune system’s response against tumors. These combined approaches offer a more powerful way to fight cancer by targeting it from multiple angles.
11. Precision oncology
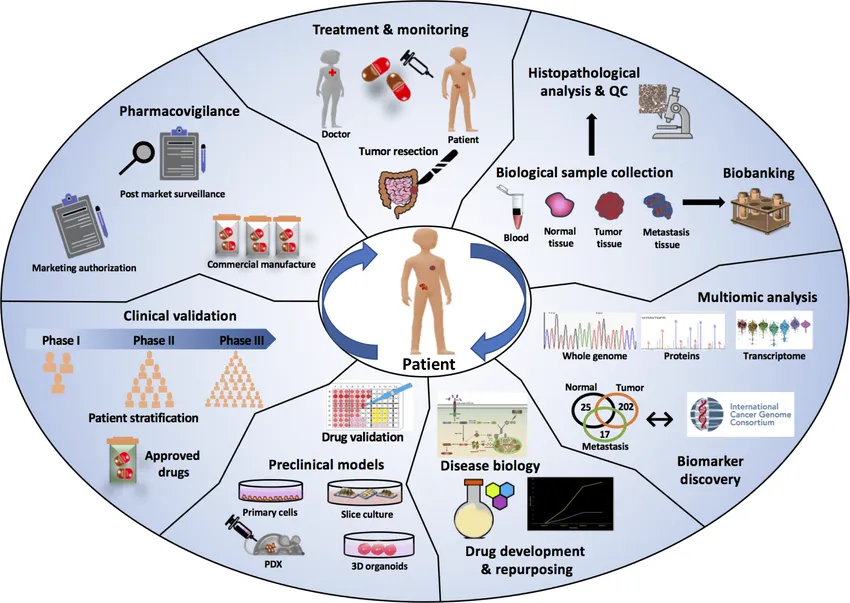
Precision oncology is being hailed as one of the best new tools in the fight against cancer, according to Sizhen Wang, CEO of Genetron Health. It involves studying the genetic makeup and molecular characteristics of a patient’s cancer. This helps doctors identify changes in the cancer cells that are driving its growth and spread. Once these changes are understood, doctors can develop treatments that are specifically tailored to the individual’s cancer. One example of this approach is the 100,000 Genomes Project in the UK, which studied over 13,000 tumor samples from cancer patients. The project used genomic data to better pinpoint effective treatments. Since precision oncology targets cancer directly, unlike general treatments like chemotherapy, it can reduce damage to healthy cells and lead to fewer side effects, making treatment safer and more effective for patients.
12. Artificial intelligence fights cancer

In India, partners of the World Economic Forum are using emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to improve cancer care. For example, AI-based risk profiling helps screen for common cancers like breast cancer, enabling earlier diagnoses. AI technology is also being used to analyze X-rays, helping detect cancers even in areas where imaging experts might not be available. These are just two of the 18 cancer interventions the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution India, in collaboration with the Forum, aims to speed up. By harnessing these technologies, they hope to make cancer detection and treatment more accessible and effective across the country.
13. Clues in the DNA of cancer
At Cambridge University Hospitals in England, scientists are uncovering new insights into the causes of cancer by studying the DNA of tumors from 12,000 patients. By analyzing genomic data, oncologists are identifying specific mutations that have contributed to each patient’s cancer, such as those caused by smoking, UV light, or internal cellular malfunctions. The scientists compare these mutations to “fingerprints at a crime scene,” as each one provides unique clues about the cancer’s origins. So far, researchers have discovered 58 new mutational signatures, expanding our understanding of cancer and how it develops. According to Dr. Andrea Degasperi, a study author from Cambridge’s Department of Oncology, this research is helping to broaden knowledge of cancer, potentially leading to more targeted treatments in the future.
14. CAR-T-cell therapy
In 2022, CAR-T-cell therapy, a treatment that prompts immune cells to hunt and destroy cancer cells, was celebrated as a breakthrough for leukemia patients. The process involves removing T cells from a patient, genetically modifying them, and then reintroducing them into the body. These altered cells produce chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), proteins that enable them to recognize and target cancer cells. Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania reported in *Nature* that two of the first patients treated with CAR-T-cell therapy were still in remission 12 years later, showcasing its long-term effectiveness. However, the US Food and Drug Administration is currently investigating whether the therapy could potentially cause secondary cancers. This comes after 33 cases of secondary cancer were reported in patients who received CAR-T therapies. While it’s still uncertain whether the therapy is to blame, a warning has been added to the packaging of the treatment as a safety measure.
Conclusion
The fight against cancer is progressing at an incredible pace, with breakthroughs happening in many areas of research. Treatments like immunotherapy and gene editing are offering new hope, while technologies like AI and liquid biopsies are revolutionizing how we detect and treat cancer. These advancements are making treatments more personalized, effective, and less harmful, giving cancer patients better chances for recovery. Although challenges still exist, the progress made in recent years is remarkable. The continued innovation in cancer research holds the promise of even greater strides in the years ahead, offering brighter prospects for those affected by cancer worldwide.
